What is vaping?
Some myths debunked.
Vaping is a term used to describe the use of eCigarettes. The use of eCigarettes is not described as smoking since by definition, smoking requires the burning/ combustion of chemicals. This does not occur with eCigarette use. The eCigarette vaporizes the eLiquid in the tank without any form of burning and this is called vaping. Therefore, eCigarette users are not considered smokers but “vapers”.
In a similar fashion to tobacco smoking, vaping also generates a cloud, inhaled and exhaled through the mouth just like smoking. However, the major difference with tobacco is that the cloud and vapour generated through vaping does not consist of burnt chemicals. A vaping cloud can be odourless and white.
The lack of combustion through vaping is thought to be one of the main advantages of electronic cigarette use over traditional tobacco smoking. The thousands of harmful chemicals generated through tobacco smoking are thought to occur as a result of the burning process that characterizes cigarette smoking that cannot be avoided. These processes do not exist with electronic cigarettes.
Electronic cigarettes have been designed since the early 2000s to be a more convenient and safer alternative to tobacco smoking. In fact, scientific research has shown that electronic cigarettes are safer than tobacco smoking.
The Royal College of Physicians (UK)2 and Cancer Research UK1 have both released statements highlighting that based on current evidence, smokers should be urged to switch to e-cigarettes, considered as a less harmful alternative.
“The hazard to health arising from long-term vapour inhalation from eCigarettes is unlikely to exceed 5% of the harm from smoking tobacco.“
“Smokers should be urged to switch to e-cigarettes, considered as a less harmful alternative.”
People should be warned of unfair comparisons that are still being made between electronic cigarettes and tobacco. This is often driven by tobacco lobbyists who have an invested interest in preventing the growth of the eCigarette industry.
1 Cancer Research UK. 10 common questions about e-cigarettes answered. May 17, 2016. Retrieved: www.cancerresearchuk.org
2 Royal College of Physicians. Nicotine without smoke. Tobacco harm reduction. April 2016. Retrieved: www.rcplondon.ac.uk
Have you ever come across the terms VV,VW, TC or TCR when looking at features of electronic cigarettes? These technical terms may appear complicated but they simply refer to the different vaping modes that can be selected on eCigarettes. Some eCigarettes may support just one vaping mode while others may support multiple vaping modes.
Direct Voltage Output
Direct voltage output, referred also as bypass mode, refers to a vaping mode whereby the voltage output is controlled automatically by the battery of the eCigarette so that the voltage output is adjusted automatically depending on the battery charge.
The higher the charge of the battery, the higher the voltage output which means more vapour is produced and inhaled by the user. If the battery charge is low, the output voltage is low and so less vapour is produced and inhaled by the user.
Standard eCigarettes support only this vaping mode while more expensive devices support this feature amongst other advanced vaping modes. Using the direct voltage output feature is ideal for those who are new to the world of vaping or those who do not want to burden themselves with adjusting the vaping settings as the eCigarette controls everything itself. It is amongst the simplest vaping modes to use, ideal for those not looking at technicalities.
Variable Wattage (VW)
Variable wattage mode, also referred as power mode, is the most common vaping mode for those who want control over there vaping experience. By increasing the wattage either through a mechanical adjustor on the battery or else through the OLED screen of the device, the user is able to control the vapour production.
Different eCigarette kits or MODs (sold individually) with the variable wattage mode feature have a defined wattage range which is often described as output wattage e.g. 5-50W. Some devices go as high to 200W and as low as 5W.
The higher the wattage, the greater the vapour that is produced at higher temperature while the lower the wattage, less vapour is produced at cooler temperature. Practically all advanced eCigarettes support this vaping mode. When purchasing an eCigarette battery (MOD) without an atomizer and using it in variable wattage, make sure that the atomizer and coil being used supports this feature.
This mode allows users absolute control over their vaping requirements. There is no “golden” wattage value and higher wattage does not mean a better vaping experience. The ideal depends mostly on your previous smoking pattern and the type of e-liquid mix being used.
Consider low wattages if you are using an eLiquid with a higher percentage of propylene glycol (PG) to vegetable glycerine (VG). Set higher wattages to have a greater vapour production if you use eLiquids with a high percentage of vegetable glycerine (VG) to propylene glycol (PG). Nicotine also plays an important role. If you use high wattage settings with high VG eLiquid and high nicotine concentrations (15mg/mL and over) and you still get a “burnt taste”, consider reducing the nicotine concentration. Learn more by clicking here.
Don’t forget, with higher wattage (higher vapour production) more liquid will be converted into vapour so you will inhale more. So you don’t require high nicotine concentrations to satisfy your cravings!
“More wattage means more vapour production (inhaled), which means less nicotine strength is required to satisfy your craving”
Variable Voltage (VV)
In this mode the voltage output of the battery is adjusted by the user to accommodate stronger or reduced amount of vapour that is produced from the eCigarette. Adjustable voltage devices have a pre-set voltage range (e.g. 2- 20V) which is then adjusted by the user. As a general rule, the higher the voltage, the higher the vapour produced and inhaled.
The voltage can be adjusted depending on the device and brand. There are two common methods: An adjustor that can be rotated manually from the bottom of the battery (e.g. Smart® Twist Kit) or in higher end devices through up and down buttons with the voltage appearing on the screen.
This vaping mode is ideal for those wanting control over their vaping experience. There is no “best” voltage as this is subjective depending on the individual taste of the user, lifestyle and type of eLiquid being used. However, users coming from a heavy smoking history may wish to start at higher voltage in order to obtain the necessary “hit” to keep away from cigarette smoking.
Temperature Control (TC)
Temperature control (TC) vaping mode is the latest novelty of electronic cigarettes. Advanced eCigarettes usually contain this feature and this allows the user to adjust the temperature of the vaping experience instead of adjusting the voltage or wattage.
Devices supporting temperature control are equipped with an advanced chip that limits how hot your coil (in the atomizer) gets based on the temperature you adjust from the screen of the battery. Due to the fact that these devices require advanced electronics, eCigarettes featuring this vaping mode are more expensive than other devices.
Vaping in temperature control (TC) mode has great benefits. First off, the liquid is never heated beyond the desired temperature, so dry hits are a thing of the past as long as this mode is used properly.
Depending on your wicking material, whether you choose organic cotton, rayon, silica, or titanium or nickel mesh they all have a burning point. By setting the temperature right below the burning point of the material you will never get a dry hit again. The instructions leaflet of your device always contains a temperature range that is recommended as a guide for users.
Not all coils/ atomizers can be used in temperature control, even if the battery module itself supports this feature. Temperature control can only be used with coils containing either Nickel, Titanium or stainless steel wire. These either come with the eCigarette or compatible ones can be purchased separately.
Important notice! Temperature Control is for advanced vapers. Always read instructions before use. Use Nickel (Ni) or Titanium (Ti) coils only in temperature control but not in wattage/ voltage modes. Do not use the conventional Kanthal coil (standard coil included in all atomizers as standard) in TC mode. Kanthal coils are to be used only in wattage/ voltage or bypass modes.
Each electronic cigarette requires the use of an electronic liquid which is vaporized (not burnt) in the atomizer to form the “cloudy white” vapour that is inhaled through the mouthpiece of the eCigarette. The electronic liquid may or may not contain nicotine. This is often represented in mg/ml on the outer bottle packaging. Nicotine is the addictive substance but is non-hazardous to human health.
eLiquid mix
In the ingredients list you may find a description such as “50% PG/ 50% VG”, which means that the eLiquid has an equal mix of propylene glycol and vegetable glycerin (VG). Both ingredients are often mixed together because they have different benefits. For example: propylene glycol is important because it enhance the flavour while vegetable glycerin creates a better “vapour cloud”. Choosing an eLiquid with non-equal proportions of PG/ VG will provide a different vaping experience and one should choose this according to his vaping preference.
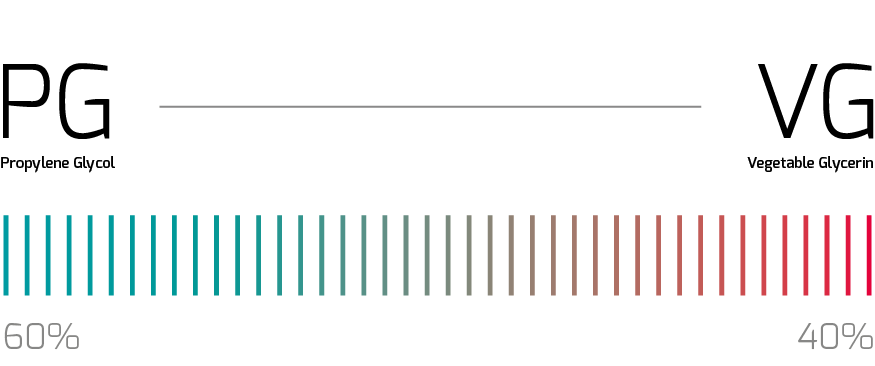
Higher % of PG
- Better flavor intensity
- Better throat hit
- Less thick liquid
- Small vapor cloud produced
- Small allergy risk
Not Ideal to be used with:
Sub-ohm atomizers / coils (less than 1ohm) as PG burns rapidly and therefore requires high resistance from the coil in order to avoid a “burnt taste”. If you get a burnt taste with eLiquid having high PG content, consider changing the coil or atomizer to one with higher resistance.
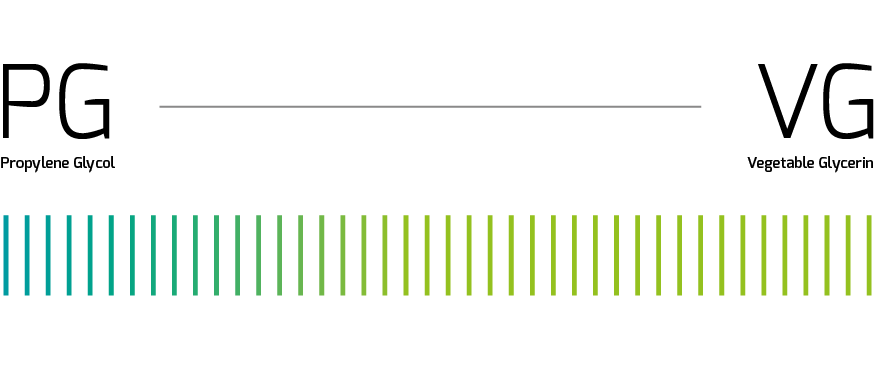
Higher % of VG
- Higher vapor density
- Thicker liquid
- Smoother feel on the throat
- Cloud chasing, the higher the VG the greater the cloud produced.
- No allergy risk
Not Ideal to be used with:
Atomizers above 1 ohm (high resistance) as this can lead to unpleasant dry hits. If you experience this change the coil to one with low resistance (less than 1 ohm).
Nicotine Strength
E-liquids come in varying nicotine concentrations to suit different needs and tastes. For many, the journey into vaping starts off utilizing high nicotine concentrations, eventually transitioning gradually to lower nicotine levels with the goal being that of getting to 0mg nicotine free liquid.
The actual concentration level of eLiquids are found on the bottles and/ our outer packaging. This is expressed in either mg/ml or percentage (%). Different eLiquids come in different concentrations depending on the brand. The most common strengths are 18mg, 15mg, 12mg, 10mg, 6mg, 0mg.
Note the rule of thumb that the greater the vapour produced from your eCigarette, the lower your nicotine content should be as more is absorbed while vaping. So if you are using an advanced eCigarette with for example a sub-ohm atomizers at high wattage (>30W) it is important to lower your nicotine strength. In these cases, 6- 12mg of nicotine can be enough to satisfy the cravings of even the heaviest smokers.




Safety
The question may arise, on whether ingredients of eLiquids may be harmful when inhaled. A study released in the Journal of Tobacco Control in 20141 has shown that the vapour released from the eCigarette of 12 different brands contained some toxic substances however these levels were between 9- 450 times lower than cigarette smoke and were, in many cases, comparable to trace amounts found in the reference ‘harmless’ product tested.
Research reviewed over 16 studies aimed at identifying whether known harmful constituents of tobacco smoking exist in electronic cigarettes. It was shown that eCigarettes are much safer than tobacco cigarettes with comparable toxicity to conventional nicotine replacement products including nicotine patches and nicotine delivery chewing gum sold in pharmacies2.
1 Goniewicz, M, L., Knysak, J et al. (2014). Levels of selected carcinogens and toxicants in vapour from electronic cigarettes. Tobacco Control, 23, 133- 139.
2 Cahn, Z & Siegel, M. (2011). Electronic cigarettes as a harm reduction strategy for tobacco control: A step forward or a repeat of past mistakes? Journal of Public Health Policy, 32(1), 16- 31.
Is second hand vaping harmful?
As a result, it is recommended that vaping nicotine containing eLiquids should be performed in either large enclosed environments or else open spaces provided local legislation does not restrict further. This would minimize the exposure of nicotine to nonusers, particularly children, pregnant women and the vulnerable population.
1Nicotine and Tobacco Research.
Is nicotine in eCigarettes harmful?
Nicotine has been reported to have health risks in the vulnerable population particularly in children, pregnancy and lactating females. As a result, it is highly recommended that no nicotine containing products including pharmaceutical nicotine replacement patches/ therapies or eLiquids with nicotine are used by vulnerable people.
There is also nicotine free eLiquids that can be used with the electronic cigarette which do not expose the user or people in the surrounding to any form of nicotine.
Will vaping help me quit smoking?
It should be stated that vaping is by definition not considered as smoking in the same way users of nicotine replacement pharmaceutical patches (e.g. Nicorette®) are not considered as smokers. This is because utilizing an eCigarette does not involve combustion as no tobacco chemicals are being burnt. As a result, by using only eCigarettes, you have essentially quitted smoking.
Scientific evidence also show that eCigarettes offer an advantage over other nicotine delivery devices, to the extent that vaping nicotine free eLiquids (e.g. 0mg nicotine eLiquids), can act as placebo, suppressing tobacco abstinence symptoms indefinitely.
1Nicotine and Tobacco Research.
Can I use vaping to quit my nicotine addiction and smoking altogether?
Why is there scaremongering surrounding electronic cigarettes and vaping?
Throughout the years, false claims have been made stating that eCigarettes are harmful to health. Amateurish media propaganda promoting such claims have also been reported. Some articles go far into saying that eCigarettes are as harmful or even more harmful than tobacco cigarettes. Such claims have never been backed by scientific research or scientific arguments and completely go against the direction of current evidence.
The tobacco industry has every interest to deter users from switching to vaping as for every switch, the tobacco industry loses business. The media sometimes falls victim of scaremongering by tobacco lobbyists so people should always read articles coming from reliable sources with the reported research ideally coming from recognized national health related organizations or registered NGOs while reported scientific data should come from reputable peer-reviewed scientific journals.
